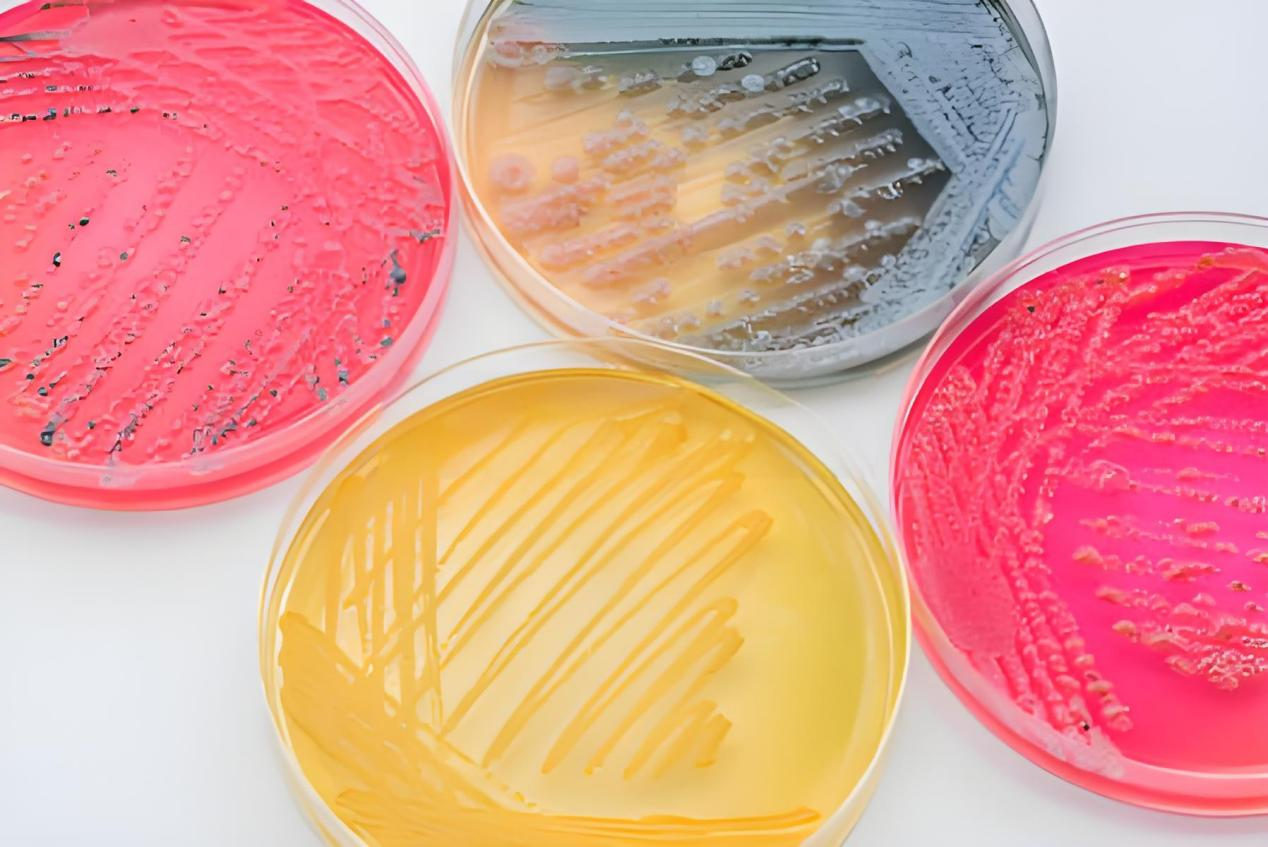
Best Culture Medium for Bacterial Growth: A Comprehensive Guide
When it comes to culturing bacteria in a laboratory setting, selecting the right culture medium is crucial for obtaining reliable and reproducible results. The choice of medium can greatly influence the growth, health, and characteristics of bacterial cultures. In this blog post, we’ll delve into the best culture media for bacterial growth, exploring their unique properties, applications, and benefits. We’ll also highlight some trending keywords and search terms related to culture media to ensure you have the most up-to-date information.
Understanding Culture Media
Culture media are nutrient solutions used to support the growth and proliferation of microorganisms. They provide essential nutrients, vitamins, and minerals that bacteria need to thrive. The selection of a suitable culture medium depends on several factors, including the type of bacteria, the purpose of the experiment, and specific growth requirements.
Popular Types of Culture Media for Bacterial Growth
- Nutrient Agar
Nutrient Agar is one of the most commonly used general-purpose media for cultivating a wide range of bacteria. It contains nutrients like peptone, beef extract, and agar, which provide a rich environment for bacterial growth.
- Advantages: Supports the growth of a variety of non-specialized bacteria; easy to prepare and use.
- Applications: Routine bacterial culture, environmental microbiology, educational purposes.

- Luria-Bertani (LB) Medium
Luria-Bertani (LB) Medium is a popular choice for growing bacteria, especially E. coli. It consists of tryptone, yeast extract, and sodium chloride, creating a nutrient-rich environment conducive to rapid bacterial growth.
- Advantages: Promotes high-density bacterial cultures; ideal for cloning and expression studies.
- Applications: Molecular biology, genetic engineering, plasmid preparation.
- MacConkey Agar
MacConkey Agar is a selective and differential culture medium designed to isolate Gram-negative bacteria and differentiate lactose fermenters from non-fermenters.
- Advantages: Differentiates between lactose fermenters (e.g., E. coli) and non-fermenters; inhibits Gram-positive bacteria.
- Applications: Clinical diagnostics, environmental testing, food microbiology.
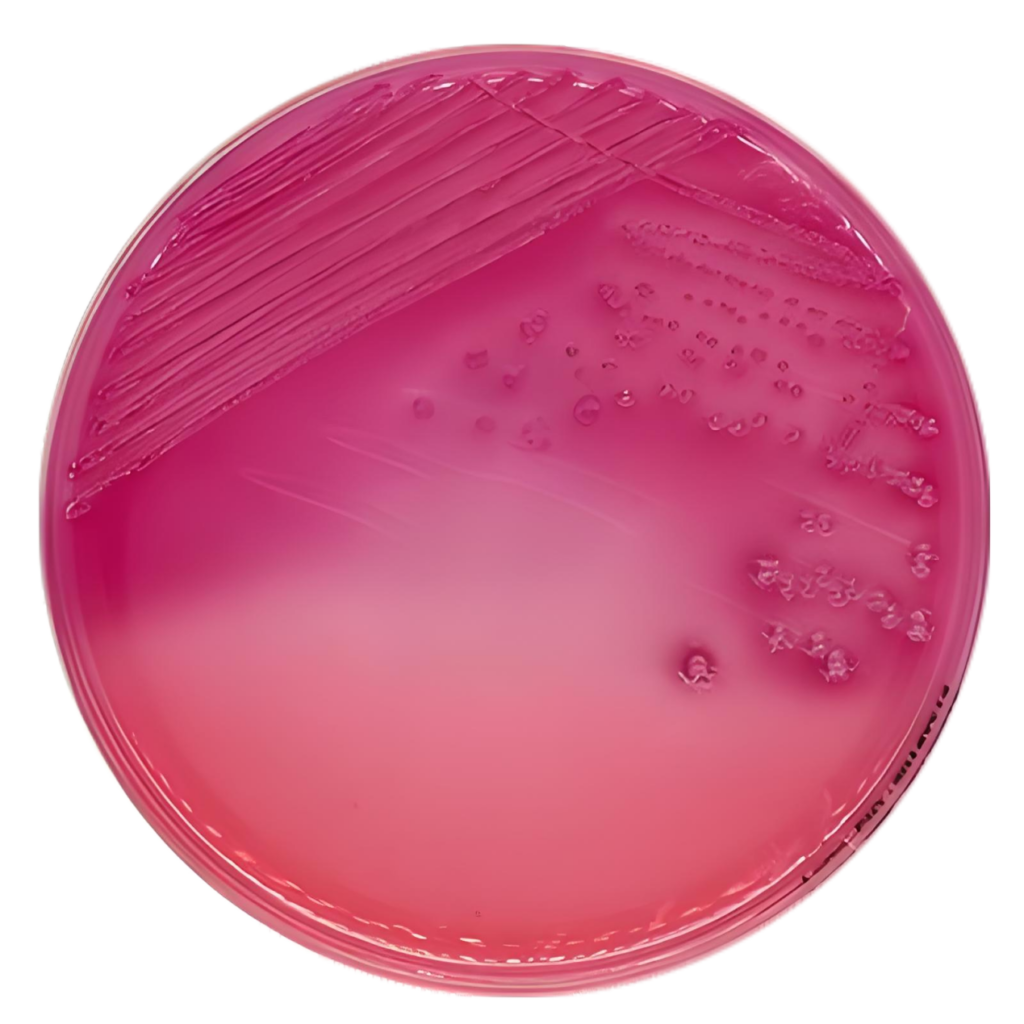
- Sabouraud Dextrose Agar (SDA)
Sabouraud Dextrose Agar is primarily used for cultivating fungi, but it can also support the growth of some bacteria. It contains dextrose, which provides a high sugar concentration ideal for yeast and mold growth.
- Advantages: Supports fungal growth; useful for isolating yeasts and molds.
- Applications: Mycology, dermatological research, clinical diagnostics.
- Blood Agar
Blood Agar is an enriched medium that supports the growth of a wide range of bacteria, including fastidious organisms. It contains sheep or horse blood, which provides additional nutrients and allows for the detection of hemolytic activity.
- Advantages: Enriches growth for fastidious bacteria; allows observation of hemolysis patterns.
- Applications: Clinical diagnostics, microbiological research, detection of pathogenic bacteria.

- Xylose Lysine Deoxycholate (XLD) Agar
Xylose Lysine Deoxycholate (XLD) Agar is used for isolating and differentiating enteric Gram-negative bacteria. It contains xylose, lysine, and sodium thiosulfate, which help in the differentiation of bacterial species based on their metabolic activity.
- Advantages: Differentiates enteric bacteria; useful in clinical and environmental microbiology.
- Applications: Pathogen detection, water testing, food safety.
Choosing the Right Medium
When selecting a culture medium, consider the following factors:
- Bacterial Type: Different bacteria have varying nutrient requirements. Use specialized media for selective growth.
- Purpose of Culture: Whether for research, diagnostics, or educational purposes, choose a medium that meets your needs.
- Growth Characteristics: Consider whether you need to observe specific traits, such as hemolysis or lactose fermentation.
Conclusion
Selecting the best culture medium for bacterial growth is a key factor in successful microbiological experiments and diagnostics. From general-purpose media like Nutrient Agar to specialized options like MacConkey Agar, each medium offers unique benefits tailored to different types of bacteria and applications. By understanding the properties and uses of various culture media, you can ensure optimal conditions for bacterial growth and achieve accurate, reliable results.
Recent Posts
- Advantages of Ready-to-Use Petri Dishes in Microbial Testing
- Top Benefits of Using Ready-to-Use Petri Dishes in Microbial Testing
- Plant Tissue Culture Media: Engineering Growth and Genetic Breakthroughs
- Chromogenic Media: Transforming Food Safety Testing Through Precision Detection
- Transport Culture Media Selection: The Science Behind Sample Stability



