
1.

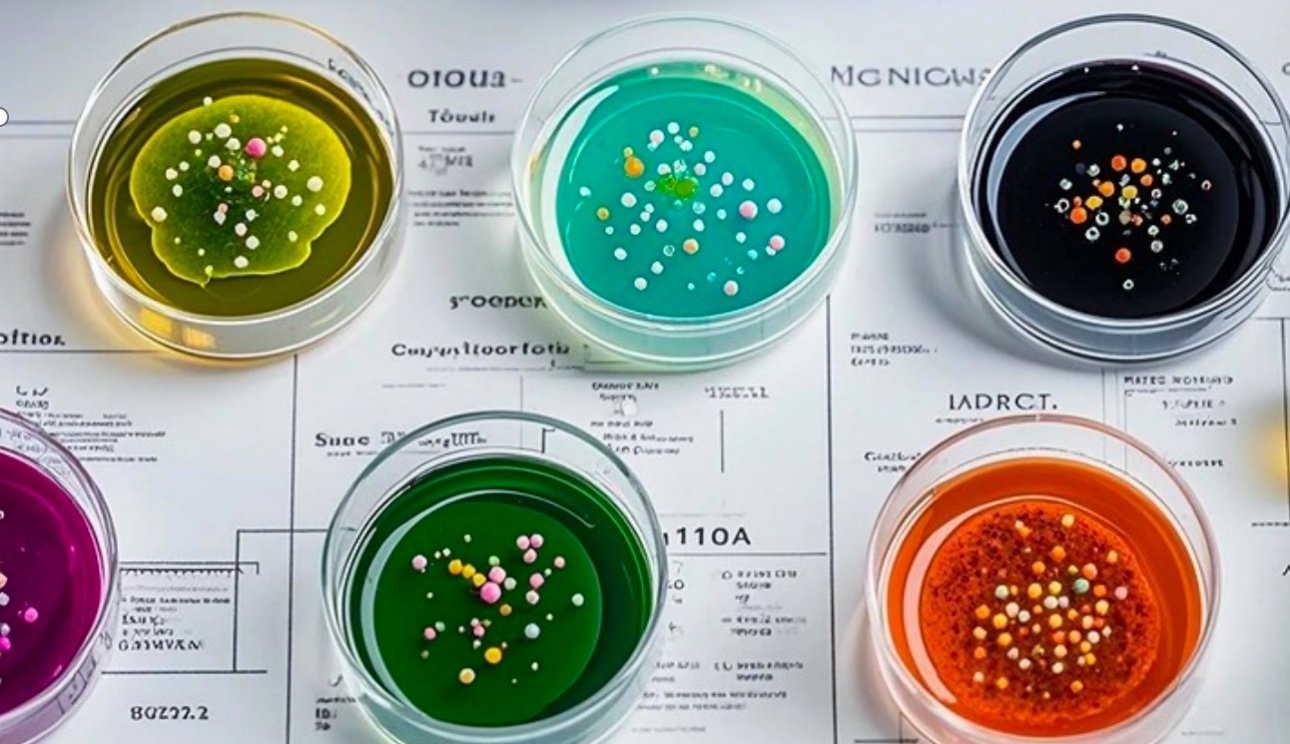
Culture medium, often referred to simply as medium, plays a pivotal role in microbiology, cell biology, and biotechnology. It serves as a nutrient-rich environment designed to support the growth, maintenance, and reproduction of microorganisms, cells, and tissues outside their natural environment.
What is Culture Medium?
Culture medium is essentially a blend of nutrients, salts, and growth factors dissolved in water or agar (for solid media). Its composition varies widely depending on the specific organism or cells being cultured and the objectives of the experiment. The primary function of culture medium is to provide essential nutrients such as carbohydrates, amino acids, vitamins, and minerals that support cellular metabolism and growth.
Types of Culture Media
There are several types of culture media categorized based on their physical state, composition, and purpose:
- Based on Physical State:
- Liquid Media: Also known as broth, liquid media are used for culturing microorganisms in suspension. They are ideal for studying microbial growth dynamics and producing large quantities of cells or metabolites.
- Solid Media: These media contain agar, a gel-like substance derived from seaweed. Agar solidifies at room temperature, providing a stable surface for the growth of microorganisms as discrete colonies. Solid media are crucial for isolating and identifying microbial species.

- Based on Composition:
- Complex Media: Contains nutrient-rich extracts such as yeast extract or peptones. They are suitable for a wide range of microorganisms that have complex nutritional requirements.
- Synthetic Media: Composed of precisely defined chemical compounds. They offer strict control over nutrient composition and are used for studying specific metabolic pathways or for cultivating organisms with well-characterized nutritional needs.

- Specialized Media:
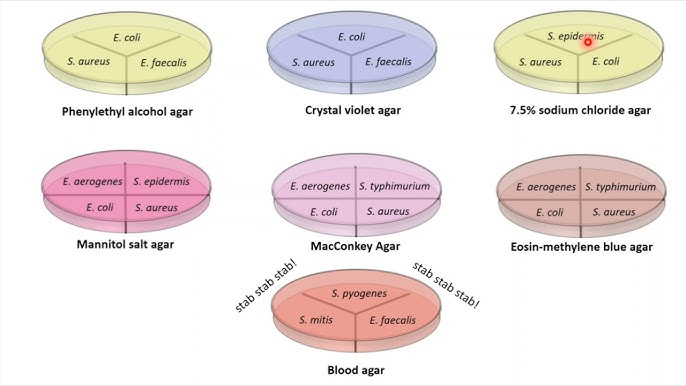
- Selective Media: Contains additives that selectively inhibit the growth of certain microorganisms while promoting the growth of others. Selective media are invaluable for isolating and identifying pathogens from complex microbial communities.
- Differential Media: Contains indicators that allow researchers to differentiate between organisms based on metabolic reactions. Examples include blood agar for distinguishing hemolytic bacteria and MacConkey agar for identifying lactose-fermenting bacteria.
How Culture Medium Works
The effectiveness of culture medium depends on several factors:
- Nutrient Composition: Ensures the availability of essential nutrients required for growth.
- pH and Osmolarity: Maintains optimal pH levels and osmotic pressure to support cellular functions.
- Sterility: Prevents contamination that could interfere with experimental outcomes.
- Growth Factors: Enhances the growth of specific organisms by providing essential growth factors like vitamins and amino acids.
Applications of Culture Medium
Culture media find applications across various fields:
- Microbiology: Studying microbial physiology, ecology, and pathogenesis.
- Cell Biology: Culturing cells for research, drug development, and biotechnological applications.
- Biotechnology: Producing enzymes, antibiotics, vaccines, and other biopharmaceuticals.
- Environmental Science: Monitoring microbial communities in natural habitats and assessing environmental health.
Conclusion
In summary, culture medium is a fundamental tool in biological research and industrial processes, facilitating the study and manipulation of microorganisms and cells in controlled laboratory settings. Its versatility and customizability make it indispensable across diverse scientific disciplines, contributing to advancements in medicine, agriculture, and environmental science.vestibulum dolor, vel commodo arcu laoreet ac. Vestibulum sed consequat purus, vitae auctor metus. Duis ut aliquet odio, at tincidunt nunc. Vestibulum dignissim aliquet orci, rutrum malesuada ipsum facilisis vel. Morbi tempor dignissim nisi. Maecenas scelerisque maximus justo eget sodales. Sed finibus consectetur vulputate. Pellentesque id pellentesque nulla. Sed ut viverra eros. Vestibulum ut ligula quam.
Recent Posts
- Maximizing Microbial Culture Success with High-Quality Media
- Advantages of Ready-to-Use Petri Dishes in Microbial Testing
- Top Benefits of Using Ready-to-Use Petri Dishes in Microbial Testing
- Plant Tissue Culture Media: Engineering Growth and Genetic Breakthroughs
- Chromogenic Media: Transforming Food Safety Testing Through Precision Detection




2 thoughts on “Understanding Culture Medium: What It Is and How It Works”
Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipiscing elit, sed do eiusmod tempor incididunt ut labore et dolore magna aliqua. Quis ipsum suspendisse ultrices gravida. Risus commodo viverra maecenas accumsan lacus vel facilisis.
Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipiscing elit, sed do eiusmod tempor incididunt ut labore et dolore magna aliqua. Quis ipsum suspendisse ultrices gravida. Risus commodo viverra maecenas accumsan lacus vel facilisis.